What is Bitcoin?
The first thing to know is that Bitcoin is both a currency and a digital system. As a currency, it can be used for everything that any currency does, but instead of having a government entity -such as a central bank- that issues and supports it, it relies entirely on the digital system that was devised by its creator Satoshi Nakamoto in 2009: the blockchain or chain of blocks.
Bitcoin is a currency just like the dollar, euro, yen, or any other local currency you can think of. It is a digital currency that only exists in the chain of blocks or blockchain that supports it and due to a sophisticated process of verification (consensus) of transactions, it cannot be spent twice. Each bitcoin -or portion of it- is unique, as each transaction is publicly recorded (although without personal data) in a large digital accounting “book” made with complex cryptographic structures, called a blockchain or chain of blocks. That is why bitcoin is called ‘cryptocurrency’, and it is only the first of its kind.
Users can manage their funds with digital wallets that have both a public key (equivalent to a bank account number) and a private key (equivalent to the bank account password). With both it is possible to carry out financial transactions from anywhere in the world and at any time. Bitcoin is decentralized, the revolution that it brings with respect to existing currencies and payment methods is that it eliminates the need for trust in central entities to be able to sustain the economy.
How does Bitcoin work?
For the average user, the operation of Bitcoin is very simple. Bitcoins are only managed in a digital wallet, which is a mobile or desktop application that can be downloaded at no cost, and from there transactions are carried out, generally free, although the procedure is usually expedited by paying a small commission that It may vary based on network congestion, transaction size, and user urgency. The most common is to wait about 10 minutes to receive between 3 and 6 confirmations that validate the transaction.
The record of the amount of bitcoins that an address has -an alphanumeric string that is equivalent to a bank account number- plus the totality of transactions carried out with its date and time can be seen publicly in a blockchain explorer, such as in this example of the portfolio where the Internet Archive receives your donations.
Comparison with other payment methods
In order to compare it against other currencies and payment methods, we must take into account certain characteristics that these two concepts present or should present to be ideal. We explore which ones below:
- Transferable and portable: It can be sent, received and loaded with ease to purchase goods and services. In some cases, it is even possible to send it to the other side of the world in just a few seconds.
- Possibility of making large transactions: It is possible to transfer large amounts to the hands of another person or entity easily and quickly.
- Possibility of making micropayments: It is possible to transfer minimum amounts – such as tips – to another person or entity easily and quickly.
- Protected against inflation: It has an established supply, that is, it is not unlimited because you cannot produce how many you want. In this way, inflation will not be a problem, because the less there are, the demand will increase and therefore the price.
- International Transactions: Can be used to send funds easily, quickly and effectively around the globe.
- Decentralized: It is not controlled by a central entity —such as the government or a bank—, and therefore it is not possible for funds to be frozen, lost or devalued according to the criteria or capacity of that entity.
- Private transactions: Ihe identity is not directly linked to the account where the funds are deposited.
- Safe: It has a certain resistance to theft and loss.
- Scalable: It can support thousands or millions of transactions per second, and continue to grow as needed.
- Divisible: It is easily divisible into many smaller parts.
- Long-lasting: Does not fade or is damaged as little as possible over time.
- Fungible: it is exchangeable for goods, services or other currencies in a proportion of equal value.
How can we use Bitcoin?
In order to use bitcoins, the first thing we must have is the required equipment: a mobile device or a PC where we can install an electronic wallet. Right away, the most obvious option is to buy those bitcoins in exchange for fiat money. And, finally, it only remains to send or even receive them.
Get a wallet
There are several options as far as wallets are concerned, and the most important characteristics in which they differ lie in their security and functionality. The most suitable option for each user is the one that can offer the necessary level of protection, but, at the same time, occupies only the resources that are available to them. However, it is important to note that bitcoins are not really stored in your wallets, but on the blockchain that is backed by thousands of nodes. The wallet is just a program that allows the owner of the funds to manage them much more easily.
We can say that a portfolio is ‘hot’ (hot) or ‘cold’ (cold), depending on whether or not it is connected to the Internet. Of course, cold (hardware) wallets are the safest. Also, we can divide Bitcoin wallets into 5 types:
- Bitcoin clients: these are the original Bitcoin wallets, for which the entire blockchain must be downloaded to the computer. Therefore, its demand for resources is quite heavy, although in return reliability, privacy and decentralization increase. We can also call them full nodes. The rest of the wallets are simple nodes (SPV).
- Mobile wallets: they are lightweight applications, designed for smartphones and tablets, usually for iOS or Android systems. They are easy to install and operate, and require little device resources. Two of them are Mycelium and Breadwallet.
- Desktop wallets: they are downloadable programs to any desktop or laptop PC, usually for Windows, Linux and MacOS systems. Three of them are Jaxx, Copay and BitGo.
- Hardware wallets: these are small devices, like a pendrive, specially designed to store bitcoins safely, offline at all times (cold wallets) and eliminating the risk of viruses that the applications may have. They are the only ones that are not free. Available brands are Trezor, Ledger and KeepKey.
- Online wallets: they are a service provided by a third party, where, unlike the others, centralization is present, that is, there is a company responsible for the validation of funds, private keys or both. Two online wallets are Blockchain and Xapo.
Beyond these five types, we can mention two additional functions:
- Paper wallets: They are called that, but they are not really wallets and may not be paper. It is simply a matter of writing down -or recording- the public and private keys on a physical medium, which can be both a designed paper that also includes a QR code -a service that Bitaddress already offers, for example- and a metal plate on which has been recorded. Bitcoins can be received in an unlimited way, but to spend them it is necessary to resort to one of the alternatives that we already mentioned.

- Multisignature function: in general, wallets include this function by which, if configured, several people are required to carry out transactions, such as in a joint bank account. All or at least several of those involved must sign to release the funds. BitPay is one of the companies that offers this alternative.
Buy and sell
Currently there are four very well defined and established ways to buy and sell bitcoins and cryptocurrencies, these are: 1.) Exchange houses, 2.) Between people 3.) ATMs and 4.) Physical stores or kiosks.
- Exchanges: the way to buy and sell bitcoins most used today is through exchange houses, which are online companies specialized in the purchase and sale of cryptocurrencies. In these you can buy several of the most important cryptocurrencies at the exchange rates set by the market. The sale of bitcoin in these can be done with or for other cryptocurrencies or fiat money (USD, EUR, JPY, among others), to suit the client.
- Natural persons (P2P): this second form of sale is possible thanks to the decentralization provided by the network, which allows the interested party to buy and sell bitcoins directly to close people, or simply acquaintances on the Internet with whom they have decided to enter into an agreement of monetary exchange. For the sale of bitcoins directly between people, who know each other or not, the interested parties should only have their respective bitcoin wallets and bank accounts, in case of exchange for fiat money.

- ATMs: several companies in various countries have installed automatic teller machines or ATMs for the sale of bitcoins, sometimes also known as BTMs. Depending on the capabilities of the ATM, you can buy cryptocurrencies for cash (the most common) or also sell bitcoins through it.
To use a bitcoin ATM, the user must have a cryptocurrency wallet on any easily mobile device. If the operation is a bitcoin purchase, the user must select said operation at the ATM, present the QR code of his wallet to the ATM reader, enter the money he wants to use in the purchase, verify the amount of bitcoins he will receive in exchange and accept the purchase.
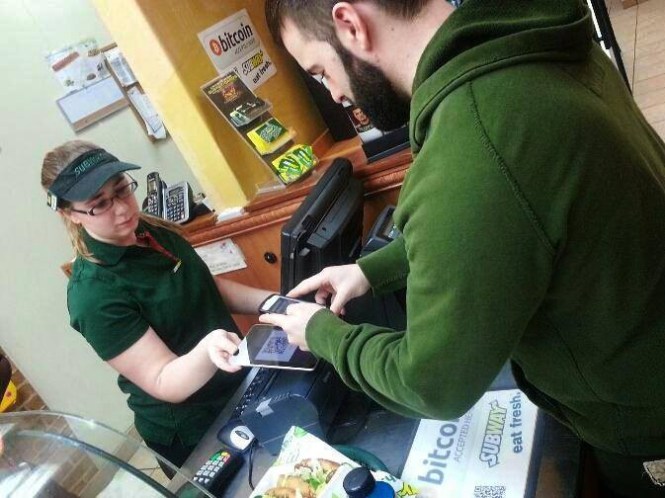
- Stores or kiosks: there are thousands of physical stores or kiosks around the world that allow you to buy bitcoins with cash or debit cards. These kiosks often require the user to fill out a form with personal and purchase information, before sending the bitcoins or delivering a paper wallet, voucher or redeemable gift card.
Like ATM operators, kiosks charge a fixed percentage on the amount of the transaction made (commonly between 5% and 16%).
Send and receive
Already with an electronic wallet, bitcoins can begin to be received. To do this, only the option to receive is chosen, and then a random alphanumeric address of 33 characters long is generated —the public key— which can be accompanied by a QR code. Either of the two data can be given to the person who is going to send the bitcoins, or put them in another purse or exchange house to be able to receive what has been purchased.
Once funds are available, we can send them to any address provided, just by choosing the option to send. There you enter the address that will receive the funds, the amount, and even the amount of the commission for the miners can be modified. The higher it is, the more priority will be given to the transaction to be included in the blockchain as soon as possible. Similarly, instead of entering the address, the QR code can be scanned with the device’s camera.

Regarding the sending and receiving to make purchases in stores, there is the possibility of facilitating the process of exchanging bitcoins for sellers through the use of payment processors. The payment processors integrate the bitcoin wallets with the benefits of the exchange houses, which makes possible the instant exchange of the bitcoins received to any currency that the platform supports. In addition, they issue invoices for the sale made.
Where can you spend your Bitcoin?
You already have a wallet with bitcoins. And now that? The truth is that, for now, it is unlikely that you can spend them at the corner store. However, the options go far beyond the online world. While it is true that you can pay directly with bitcoins in many web stores, such as Microsoft, Dell, Expedia and G2A; or buy gift cards that can be spent on sites like Amazon, iTunes, Starbucks or eBay; This does not mean that there are not numerous physical stores where cryptocurrency is accepted.
In fact, there are web pages that function as maps to find these businesses all over the world. One of them is CoinMap, where 9356 stores of all kinds are registered globally, including restaurants, mechanics, art galleries, computer stores, travel agencies, clothing sales, clinics and much more. With bitcoin you can buy from a hamburger or a sandwich to rent a Ferrari or buy a motorized unicycle. On the contrary, you can decide to save them as a store of value – since it is not surprising that their price increases over time – or send them to a relative as a remittance to another country, quickly, easily and safely.
And the places that accept bitcoins are increasing more and more. Its adoption has skyrocketed in Japan, as well as in Russia and Spain. To find where to spend your bitcoins, you just have to look near you on the map.
Is Bitcoin Legal?
Bitcoin is generally not illegal, but it all depends on each jurisdiction. Its legal status, currently, is in full development throughout the world, so it is very usual that in most countries it is still in the middle of a legal vacuum in which the principle of prohibition of Hans could well be applied Kelsen: “everything that is not prohibited is allowed”.
In others, like Japan, it already has an established status as a payment method – and not as a currency – and has been regulated for merchants, in order to prevent it from being used to commit crimes such as money laundering and terrorism. In the UK, on the other hand, it is treated as currency (foreign currency). In Spain it is considered a digital good, so it is governed by the laws of exchange of goods. In Latin America it is not considered a legal tender, but it is not regulated. In Illinois (United States) it is not recognized as currency either, so it is free of regulations; Although, for its part, the country’s Internal Revenue Service (IRS) treats it as merchandise, for which its holders must pay taxes.
Only in Bangladesh, Bolivia, Ecuador and Kyrgyzstan is it officially prohibited, while in China, New York and Canada it must be governed by strict regulations.
Of course, bitcoin has been closely linked to the Darknet and has unfortunately become known as the hacker’s currency, due to its pseudo-anonymity and the fact that no document is required to open a wallet and own as many units as you want , has been a useful tool for many criminals. However, it should be noted that bitcoin is money, and like all money, it can also be used for any purpose. For this reason, many authorities around the world are building a legal framework that allows its use and prevents, at the same time, the financing of crimes.






